Introducing Ezno
Ezno is an experimental compiler I have been working on and off for a while. In short, it is a JavaScript compiler featuring checking, correctness and performance for building full-stack (rendering on the client and server) websites.
This post is just an overview of some of the features I have been working on which I think are quite cool as well an overview on the project philosophy ;)
It is still work in progress, all the examples work but the tool is still in its infancy
Type synthesis and checking
The core of Ezno is a type checker for JavaScript. Type synthesis is analysing syntax and formulating properties of terms. Comparing the information on terms and how those terms are used, a type checker can prevent errors at runtime.
Ezno's type checker is built from scratch. Getting the features I wanted required a lot of different functionality and needed several new ideas that as far as I know aren't present in any system or existing checker. The checker is fully compatible with TypeScript type annotations and can work without any type annotations at all.
You can think of it as an extension to TSC, similar ideas but taken further
The next few sections go into some unique features of the checker before going into the real benefit of having all this information about types.
Dependent typing
One of the key ideas with Ezno is that it attempts "maximum" knowledge of a source. This knowledge includes:
- Runtimes exception that could happen because of missing properties
- Code that will never run
- Expressions that could be collapsed to reduce work
- Mutations to data
Because of the dynamism of JavaScript, this requires including references to constants (aka known numbers, booleans, strings, etc) in the type system.
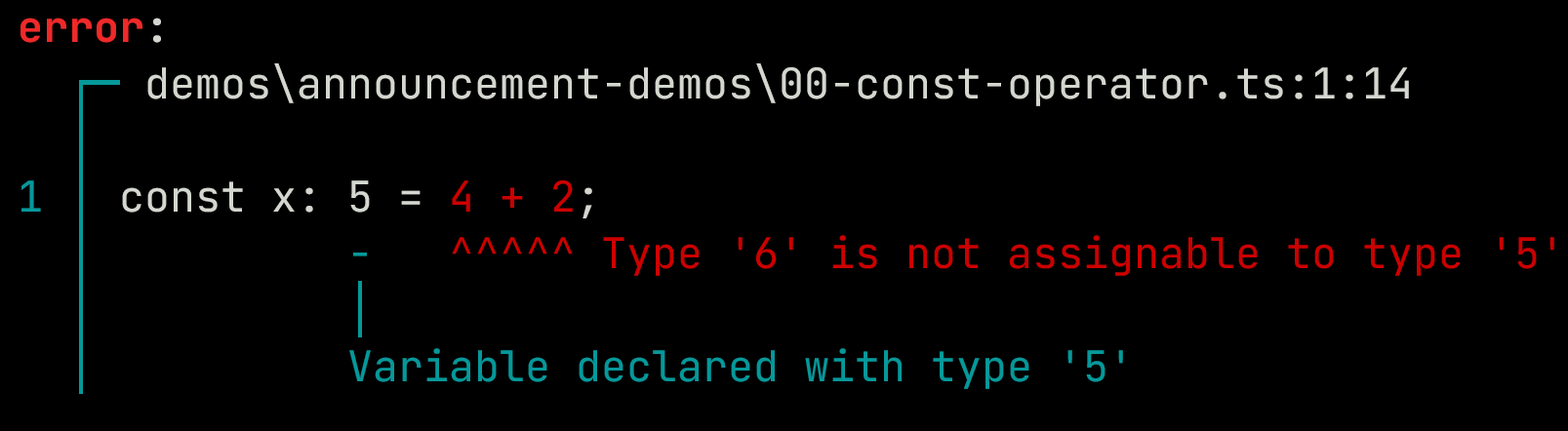
While TypeScript includes dependent types, Ezno has built on top of that doing more such as constant operator evaluation.
const x: 5 = 4 + 2;
const x: 5 = 4 + 2;
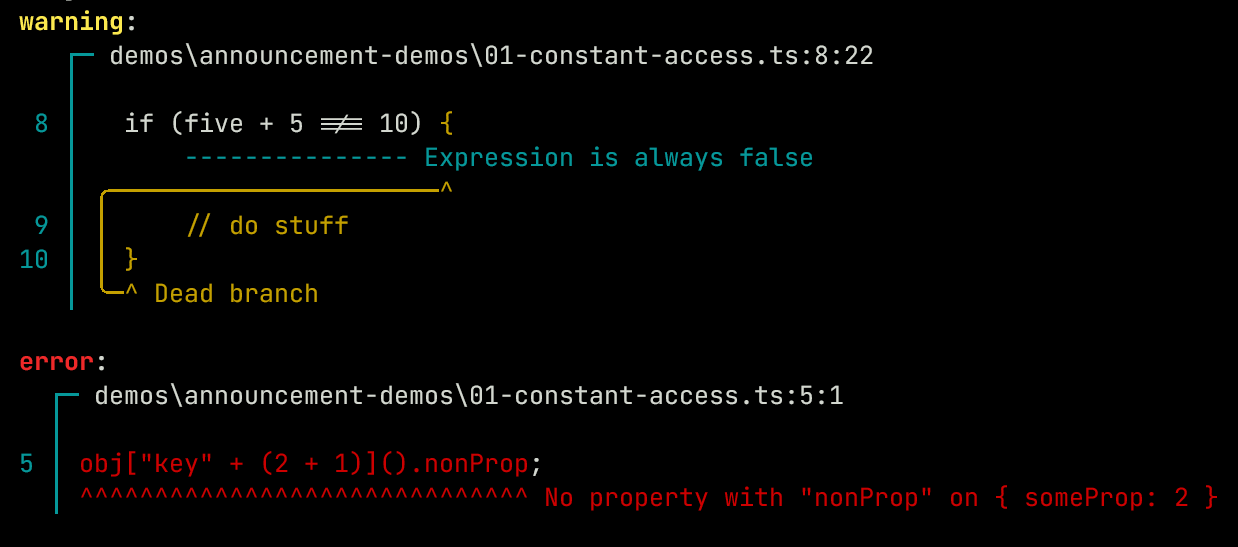
Scaling this up you can now see this working for both identifying an invalid property and detecting dead code:
const obj = {
key3() { return { someProp: 2 } }
}
obj["key" + (2 + 1)]().nonProp;
const five = 5;
if (five + 5 !== 10) {
// do stuff
}
const obj = {
key3() { return { someProp: 2 } }
}
obj["key" + (2 + 1)]().nonProp;
const five = 5;
if (five + 5 !== 10) {
// do stuff
}
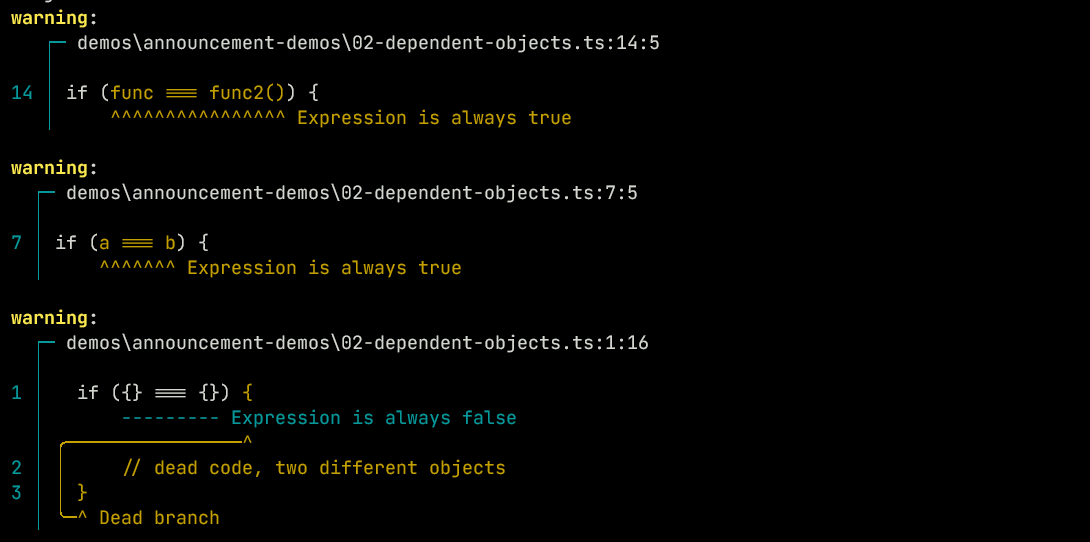
Objects
As well as identifying terms like 4 and "hello", Ezno also treats objects and functions as constant terms:
if ({} === {}) {
// dead code, two different objects
}
const a = {};
const b = a;
if (a === b) {
// always true, reference to same object
}
function func() {}
function func2() { return func; }
if (func === func2()) {
// always true 👀
}
if ({} === {}) {
// dead code, two different objects
}
const a = {};
const b = a;
if (a === b) {
// always true, reference to same object
}
function func() {}
function func2() { return func; }
if (func === func2()) {
// always true 👀
}
Making all function parameters generic/dependent
While the examples showcase great static analysis of a sequence of statements. Synthesis can be more difficult when it breaks into functions and knowing what happens across call sites. Ezno can trace the flow of data and actions on it by treating every parameter as what most languages refer to as generic:
function addOne(x: number): number {
return x + 1;
}
const three = 3;
const four = addOne(3);
assertType<4>(four);
function addOne(x: number): number {
return x + 1;
}
const three = 3;
const four = addOne(3);
assertType<4>(four);
Here the
addOnefunction is annotated that it returns anumber. But instead internally in Ezno the actual result is what it synthesised that it returned. Thenumberin the return type is only used as a constraint on the type returned in body. The synthesised return type that Ezno uses in this case isAdd<T, 1>. In total Ezno internally views the function as:addOne: <T extends number>(x: T): Add<T, 1>
Untyped parameters
Parameters that don't have a type annotation have inferred constraints based on usage in the function body. The simplest is a function with no constraints:
function id(a) {
return a
}
assertType<number>(id(2));
assertType<string>(id("Hello World"));
assertType<"x">(id("x"));
function id(a) {
return a
}
assertType<number>(id(2));
assertType<string>(id("Hello World"));
assertType<"x">(id("x"));
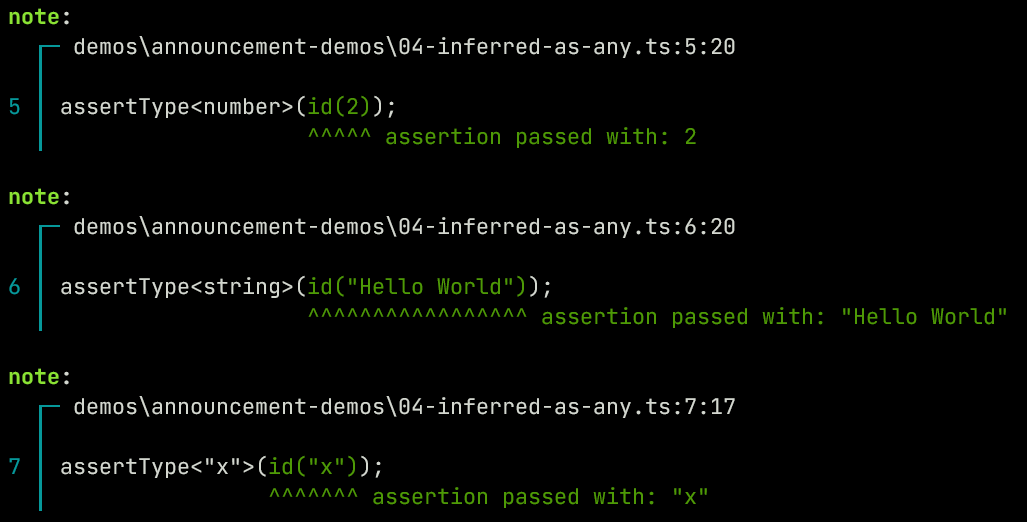
Here when the
idfunction is synthesized it infers theaparameter as being generic and thus the function takes the type<T extends any>(a: T) => T.
Inferred generic restrictions
In the above usage, the constraint of parameter a is initialized as any. Its usage in the block didn't require narrowing it down so it stayed as any. Now moving on to a slightly more complex function:
function runMap(obj, func) {
return obj.map(func)
}
function runMap(obj, func) {
return obj.map(func)
}
Here initially obj and func are generics that alias any. However, usage of the obj parameter has inferred for the runMap to be type safe obj must have a map property and that map property must be callable with func:
runMap({}, v => v);
runMap({}, v => v);
This is because the .map synthesis changed the alias. The function is synthesized to <T extends { map: (a: U) => any }, U>(obj: T, func: U) => T["map"](U). (where the return type is the call of obj.map with parameter U).
assertType<Array<string>>(runMap(myArray, v => v));
assertType<4>(runMap(
{ map(cb) { return cb(2) } },
v => v + 2
));
assertType<Array<string>>(runMap(myArray, v => v));
assertType<4>(runMap(
{ map(cb) { return cb(2) } },
v => v + 2
));
It is important to note that Ezno isn't the first JavaScript type checker that has inferred generics. Hegel infers generics for functions. However I when tried on the above example with its more complicated two levels of inference, Hegel could not figure it out.
The benefit here with generics is that the function can be very expressive and dynamic, but the function still passes off maximum information to the scope where the call occurred.
Free variables (hidden parameters) of functions
The usage of this is a hidden parameter to functions, it is specified by the bounded structure rather than arguments at the call site. Here Ezno treats it as generic but separate from actual parameters:
function getThis() {
return this
}
assertType<Window>(getThis());
assertType<2>(getThis.call(2));
function getThis() {
return this
}
assertType<Window>(getThis());
assertType<2>(getThis.call(2));
Variables in parent scopes work similarly to this. Rather than being passed through the call site it instead exists in a parent of the current environment as:
let a = {};
function x() {
a.doThing();
}
x();
a.doThing = () => console.log("Hello world");
x();
let a = {};
function x() {
a.doThing();
}
x();
a.doThing = () => console.log("Hello world");
x();
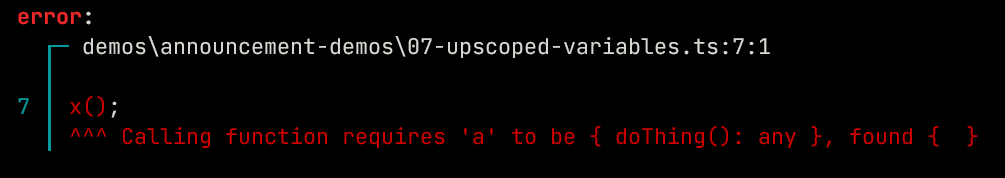
This works using the same generic system that function parameters use. For variables without a type annotation on the variable, it reuses the inferred generic system.
The example above also shows a sneaky feature of Ezno...
Effects/events
One of the problems of JS is that functions can be impure. Impure means it can apply side effects that are not tracked through the returned type.
Ezno tracks side effects that a function may perform:
const data = { x: 0 };
function getFive(obj) {
obj.x += 1;
return 5;
}
assertType<0>(data.x);
assertType<5>(getFive(data));
assertType<1>(data.x);
const data = { x: 0 };
function getFive(obj) {
obj.x += 1;
return 5;
}
assertType<0>(data.x);
assertType<5>(getFive(data));
assertType<1>(data.x);
Here this function data-wise returns a number with proof of it being equal to 5. But there are additional "effects" that aren't encoded into that return type. When synthesizing functions Ezno tracks mutations through a system in the context/environment called events. Events in a function then get associated with the function referring to the "effects of the function".
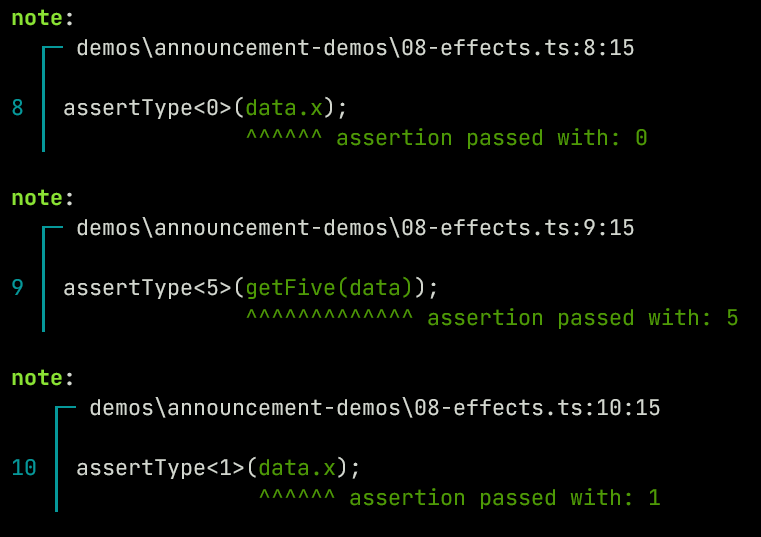
The events sequence is sort of a typed intermediate representation and is additionally used for optimisations involving used assignments and such. This has some similarities to SSA. But it is integrated into the checker and is based on types.
Constant functions
Ezno treats function uniquely with a pointer to a function instead of just a "shape" (the same way constant terms and object references work).
We have seen some calculations on operators being calculated at compile time, but the idea carries over to many internal functions. This means it has a direct binding to the function. From this, it can be definitively known that this function is Math.sqrt allowing the following to work:
let x: 2 = Math.floor(Math.sqrt(5));
let x: 2 = Math.floor(Math.sqrt(5));
This applies to more functions than just that in Math. The following also applies to many other functions in the standard library. Here we see effects, this treated as generic and constant functions at play:
const myObj = {
name: "hello world",
uppercase() {
this.name = this.name.toUppercase()
}
};
assertType<"hello world">(myObj.name);
myObj.uppercase();
assertType<"HELLO WORLD">(x.name);
// Also explicit this calling:
const otherObj = { name: "make me upper" };
myObj.uppercase.call(otherObj);
assertType<"MAKE ME UPPER">(otherObj.name);
const myObj = {
name: "hello world",
uppercase() {
this.name = this.name.toUppercase()
}
};
assertType<"hello world">(myObj.name);
myObj.uppercase();
assertType<"HELLO WORLD">(x.name);
// Also explicit this calling:
const otherObj = { name: "make me upper" };
myObj.uppercase.call(otherObj);
assertType<"MAKE ME UPPER">(otherObj.name);
JSX
Ezno has support for JSX syntax. A key part of this implementation is that it treats different tags as different tags:
assertType<HTMLParagraphElement>(<p>Paragraph tag</p>);
assertType<HTMLParagraphElement>(<p>Paragraph tag</p>);
It also records more information about the relation of elements to interpolated data and event listeners. (Using the same system that Ezno uses to identify unique objects).
const a = <p onClick={(ev) => {
assertType<HTMLParagraphElement>(ev.currentTarget);
}>Paragraph tag</p>;
const a = <p onClick={(ev) => {
assertType<HTMLParagraphElement>(ev.currentTarget);
}>Paragraph tag</p>;
You can think of these as being similar to objects with properties. But in this case, the children binding follow through:
function LazyImage(href: string) {
return <img href={href} loading="lazy">;
}
const myImage = LazyImage(myInput);
assertType<true>(myImage.getAttribute("href") === myInput);
function LazyImage(href: string) {
return <img href={href} loading="lazy">;
}
const myImage = LazyImage(myInput);
assertType<true>(myImage.getAttribute("href") === myInput);
Which leads on to the reason for adding these bindings:
The "framework"
One of the biggest uses of JS is with declarative user interface programming.
React is one of the most popular libraries for declarative interfaces. However, its internals are computationally expensive. With Ezno one of the goals was to provide enough static analysis to work with the expressiveness of React but use the information to make it do a lot less work.
"framework" is a temporary name for the plugin written on-top of Ezno, Ezno is not the framework. The "framework" is a plugin using logic from the parser and checker and is entirely detachable.
Eliminating the need for a Virtual Document Object (VDOM)
Firstly, a definition of the VDOM (from my web definitions post):
The virtual DOM is a structure akin to the DOM. It is slimmer and has a subset of the API of the structures defined in the DOM JS spec e.g.
HTMLElement.VDOM is a virtual representation of the document, actual DOM references the document (e.g..click()isn't on VDOM structures).It is used to add to or update the existing actual DOM/UI.
When the application state changes it recreates the UI by rerunning functions that generate VDOM and use a the difference between the new result with a previous result to make changes/reconcile to the actual DOM/UI. This is a declarative style of programming, where the UI is a map from the state to UI. It is often simpler than manually writing the imperative updates to the document at every state change.
The VDOM isn't free
Before we go into eliminating it we have to deal with the why? As well as the downsides that should occur in the alternative.
Every time an update to the state happens, the runtime needs to rebuild the UI whole tree. This is necessary to find that any of the nodes have changed, but the majority of the new UI hasn't changed and you have to create and store duplicate nodes. The UI can require evaluating expensive calculations that often return the existing value.
Memoization partially solves this, parts of the tree can be wrapped and when compute them it looks for cached versions of the computation. While this solves the recreation time there is additional memory overhead to hold the cached results and hashing and lookup is not free. It is also developer overhead to realise what is static and independent. Extra explicit-ness in the syntax (unless a auto memoising compiler was added), just overall more complicated.
Additionally, to do this handling with the VDOM the library has to be shipped with a reconciler on top of the state handler and the diffing algorithm, all leading to larger JS payloads. There is also the process of starting up the client after SSR. Unless event listener delegation is used ahead of time, when adding event listeners to existing markup VDOM it requires a representation of the whole tree to find event listeners. And even if the event listeners are delegated, a VDOM framework requires creating the existing UI tree to perform updates on an existing server-rendered tree, which requires loading the whole state.
VDOM without the VDOM
One of the questions for this project was 'What analysis do you need to do to use JSX and the full range of JS expressions that React works with, without running into the complexities and execution expensiveness of a VDOM?'.
Because of the tracking of poly-types in Ezno's checker, the values passed around useState can be reasoned with. For example this is what is tracked from the left and right values from a useState call.
const [value, setValue] = useState("");
// value : any (via dynamic constraint)
// / [0]
// useState("")
// \ [1]
// setValue : (any) => any
const [value, setValue] = useState("");
// value : any (via dynamic constraint)
// / [0]
// useState("")
// \ [1]
// setValue : (any) => any
Because of this, we have three unique types created from this statement that can be tracked.
return <>
<input onChange={ev => setState(ev.target.value)}>
<p>{value}</p>
</>
return <>
<input onChange={ev => setState(ev.target.value)}>
<p>{value}</p>
</>
Building a compiler to generate imperative calls is then very simple:
- Find calls where a function calls the state a function that modifies state (for example
useState()[1]) - Lookup element points (attributes, children, etc) that are of a type where the base
useStateis the sameuseState()[0](type synthesis stores reverse references on objects) - Replace
setStatecall with direct DOM updates that affect the element points
These updates are relative to the elements in the DOM as these relationships are found during the type synthesis. Therefore the above would generate something similar to:
input.addEventListener("change", ({ target }) => {
target.nextElementSibling().innerText = target.value;
});
input.addEventListener("change", ({ target }) => {
target.nextElementSibling().innerText = target.value;
});
Here the type information enables generation of this direct update instead of relying on a VDOM at runtime to find this change.
State objects
const value = useProxy({ count: 2 });
function updateCount(value) {
value.count++;
}
return <span>{count}</span>
const value = useProxy({ count: 2 });
function updateCount(value) {
value.count++;
}
return <span>{count}</span>
This sort of thing works in valtio and is the previous implementation in my old framework Prism. This is possible using Proxies at runtime, but suffer from many complications at runtime.
Because of effect tracking in Ezno, it becomes fairly straightforward to find state mutations across functions so these updates can be found and inlined similar to the above. The uniqueness of functions here enables special handling of .map and .push as they are known to be array methods after the type synthesis.
const value = useProxy({ items: [] });
return <ul onClick={() => value.items.push(new Date())}>
{value.items.map(item => <li>{item}</li>)}
</ul>
const value = useProxy({ items: [] });
return <ul onClick={() => value.items.push(new Date())}>
{value.items.map(item => <li>{item}</li>)}
</ul>
From this, the logic can work out that calling .push appends a new element to the ul element. Therefore it can skip over needing keys and finding list differences in this scenario and generate a simple .appendChild call.
Universality, adding event listeners and hydration
Most frameworks enable some sort of server-side rendering (often abbreviated to SSR). SSR is the functionality in the framework to generate a HTML string representation of the same UI under a state identically to the result on the browser. It is also used in static site generation where the build tool runs all the requests at build time and saves the results to some sort of static output.
As Ezno knows about bindings and the type interpolated, that information can be used inside the compiler to hydrate the state from the rendered HTML.
const [a, setA] = useState(0);
<button onClick={() => setA(a => a + 1)}>{a}</button>
const [a, setA] = useState(0);
<button onClick={() => setA(a => a + 1)}>{a}</button>
button.addEventListener("click", ({ target }) => {
target.innerText = parseInt(target.innerHTMl) + 1;
// ^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^
// Here is the reverse expression. Again it knows about types so can invert the implicit cast of a integer to a string
});
button.addEventListener("click", ({ target }) => {
target.innerText = parseInt(target.innerHTMl) + 1;
// ^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^
// Here is the reverse expression. Again it knows about types so can invert the implicit cast of a integer to a string
});
For upgrading existing HTML, rather than each element registering an event listener (which can result in hundreds of addEventListener calls) it instead can a single one at the top level. The output of the framework is still a work in progress but with the bijective property map, the position of elements works without the notion of components.
createRoot(document.body).render(() => <>
<button onClick={() => console.log("clicked")}>Log click</button>
<button onClick={async () => { await fetch("/do-thing") }}>Make request</button>
</>);
createRoot(document.body).render(() => <>
<button onClick={() => console.log("clicked")}>Log click</button>
<button onClick={async () => { await fetch("/do-thing") }}>Make request</button>
</>);
possible compiled output:
document.body.addEventListener("click", async ({ target }) => {
const id = target.getAttribute("data-click");
if (id === "0") {
console.log("clicked")
} else if (id === "1") {
await fetch("/do-thing")
}
});
document.body.addEventListener("click", async ({ target }) => {
const id = target.getAttribute("data-click");
if (id === "0") {
console.log("clicked")
} else if (id === "1") {
await fetch("/do-thing")
}
});
Other ideas
Some other ideas that type information can enable:
Server-side rendering out of the JavaScript runtime
One of the problems with JavaScript frontend server rendering implementations is that SSR/"string builders" run on JavaScript which means they are locked into a server runtime like Node or Deno. This is perfectly fine for most things but I think this is generally quite a heavy restriction, which prevents using a lot of cool backend technologies written in other languages like Rust, Python etc. Some tools have embedded a JavaScript runtime into the application (such as rusty_v8). However, joining these two systems together can lose type safety bridge and data often has to be copied into the runtime which seems to void the performance improvements.
With type information, it could allow Ezno to generate some format that is tightly integrated with the server language. This is quite simple to do for string elements and Ezno knows the shape of data and the pointer to every function it could easily transpile some of this stuff. However, it is still up in the air how this would work if the server has to do something more complicated mutating data and I don't have a clear idea of what the format would be that could be used across languages would look like.
Auto progressive enhancement
As Ezno knows at compile time what functions have been bound to certain event listeners plus the internal effects it knows to extract runtime state mutations to the server to add a backup to client-side interactions if JavaScript fails to load.
Plugins and extensibility
Ezno is written in Rust and has several places/hooks for adding additional functionality:
Exterior type safety
Because Ezno treats functions as unique it allows for special handling of functions via Ezno's plugin system.
For example, the fetch function could be overridden and known strings could return a more precise type based on knowledge of what an endpoint returns.
Build tool front-ends
Aside from the CLI, there is a language server plugin (LSP) so you can use it in an editor. For those who don't like the command line build step, there is a half-working Nodejs runner, this means you can integrate the build step into the runner compressing running the source into a single command. For the web, there is a WASM service worker runner that shouldn't need to touch the filesystem during development.
Complexity & wrapping up the features
Enough with the features here is a roundup and some philosophy of the project
Types
Types are an integral part of JavaScript with features like instanceof and typeof. TSC, Flow, Hegel, Ezno and other checkers reason with this runtime behavior ahead of time, which can help find errors before they find themselves. However, unlike JavaScript this ahead of time behavior isn't specified and so each checker has different approaches to what and how it should emit type errors.
Places where Ezno diverges from TypeScript
Given TSC has the largest share in the JavaScript type checking ecosystem, I think it is really beneficial for Ezno to be usable in projects currently using TSC. Many of the ideas from TSC have been included in Ezno, with Ezno going the extra mile in many cases to be more sound so that it can use type-information for build time optimisations.
One of the big things is that Type annotations in source code are treated as restrictions under Ezno and so are not strictly necessary. Ezno prefers to use the JavaScript as the source of truth. From the previous section on events and generic calls, the information needed to generate more accurate results is more complex (and verbose) than simple annotations allow, thus why it is prefered to generate this from the JS code rather than require nnoations.
Also, TypeScript has allows breaking out the type system by the any type to be cast as a specific type (such as string in the following example).
// Passes under TSC
function y(a: any): string {
return a
}
y(2).slice(2)
// Passes under TSC
function y(a: any): string {
return a
}
y(2).slice(2)
Implementing any this way makes TypeScript easier to adopt and allows things to compile in weird environments. However for Ezno to do its optimisations this magic any type that has the property of all types without narrowing doesn't quite work.
Don't take Ezno's features as a knock on TypeScript, TypeScript is great. Ezno started as a pet project to reimplement the features of TSC in Rust. But as things started to go well after adding more and more TSC features, it was apparent that optimisations such as the hydration and the reactive systems weren't going to be possible directly following its path. It isn't possible to detect what can happen to the state when called through a term that represents any. TypeScript holes aren't particularly critical if you just want code completions and some basic errors to be caught. They allow the more complex parts to not be blocked by compiler errors. But for doing optimizations a single unknown result can make it impossible.
The hope is with diverging and trying to extend TSC will help in staying up to date with newer TypeScript features (as it will be ahead, rather than behind).
Currently Ezno isn't a feature-complete type checker. There are still a lot of things to still work on. So far the first section goes over the analysis of completely static code. The next step is to apply these ideas to more dynamic structures. There are also some ideas not mentioned here to prevent this post from being too long 👀.
Frameworks
The output of the framework is still a work in progress. There are still a few things to add to the type checker that are necessary to get "the framework" plugin to work in edge cases. Thus no benchmarks or definite output in this post. Most benchmarks show hand-written JavaScript code to be the most efficient so the idea is to take the syntax and information about it to squeeze it into the closest of the hand-written forms. The performance gains from all these optimisations are probably unnoticeable. This is an exercise in attempting to get to the least amount of code to run to make a page interactive.
Some frameworks abstract through libraries and the structure of functions. Some compiler-based frameworks abstract through syntax. Ezno's framework is unique it is based on data and the semantics of the program above what is visible from the syntax.
Ezno today
I think it is fun short and quirky and most importantly, not taken on package registries.
I want to keep things moving but slowly. I think incomplete projects are good as they have space to add additional features and improve. Some projects I see which seem closer to their goal have less space to improve. I think some tools are built too quickly and I don't want Ezno to fall into that category.
No demo binary out yet, need to finish off some things on more advanced events to get some of the cooler demos to work. Hoping for something demonstrable before the end of this year 🤞